Compressors Pumps
| Standard | Markets | Parameter | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
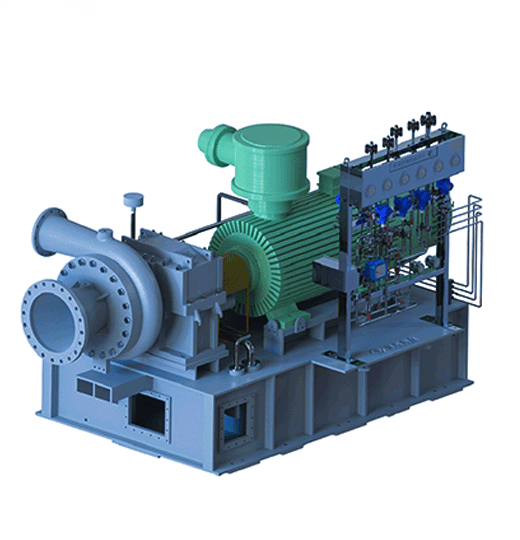
RCY-M Compressor Spectrum | API610-ISO13709 |
|
|
|
|
RCY-L Compressor Spectrum | API610-ISO13709 |
|
|
|

|
Ingersoll Rand C3000 Air Compressor | ISO 8573 |
|
|
About Compressors Pumps
Compressor pumps are mechanical devices that increase the pressure of a gas, while pump compressors are devices that move fluids by increasing their pressure. Both types of machines are commonly used in industrial and commercial applications to power pneumatic tools, operate machinery, and transport fluids. Compressor pumps typically work with gases such as air, while pump compressors handle liquids such as water or oil.
How Does a Compressors Pump Work?
Compressor pump works by drawing in air or gas and then compressing it to increase its pressure. This is done by using a piston or rotor to reduce the volume of the air or gas, which causes its pressure to increase. The compressed air or gas is then stored in a tank or released through an outlet for use in various applications such as powering tools or inflating tires.
Compressors Pump Terms
To obtain a clearer understanding of compressors pumps, it’s helpful to examine the various terms associated with them. The most common terms used include:
- Discharge pressure: The pressure at which compressed air is delivered from the compressor.
- CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute): A measure of the volume of air that a compressor can deliver per minute.
- Horsepower (HP): A measure of the power output of the compressor's motor.
- Duty cycle: The percentage of time that a compressor can run in a given period without overheating or causing damage.
- Tank size: The volume of the air storage tank on the compressor, measured in gallons.
- Oil-free vs oil-lubricated: Refers to whether the compressor uses oil as a lubricant for its moving parts.
- Single-stage vs two-stage: Refers to the number of compression stages the compressor has, with two-stage compressors providing higher pressures.
- PSI (Pounds per Square Inch): A measure of the pressure of the compressed air.
- SCFM (Standard Cubic Feet per Minute): A measure of the volume of air that a compressor can deliver per minute, standardized to a specific temperature and pressure.
- Compressor efficiency: The ratio of the amount of energy put into the compressor to the amount of energy delivered as compressed air.


